TYPES, NATURE OF CONFLICTS, AGENT COSTS AND RESOLUTION IN AGENT RELATIONSHIP IN AN ORGANIZATION
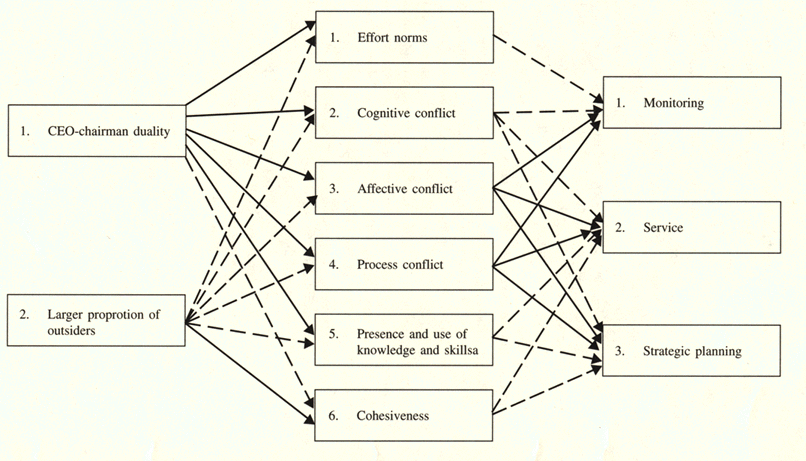
The agency theory attempts to explain the conflicts of interest among corporate constituencies, including those between corporate ‘insiders,’ such as controlling shareholders and top managers, and ‘outsiders,’ such as minority shareholders or creditors. These conflicts all have the character of what economists refer to as ‘agency problems’ or ‘principal-agent’ problems. ‘Agency problem’—in the most general sense of the term—arises whenever the welfare of one party, termed the ‘principal’, depends upon actions taken by another party, termed the ‘agent.’ The problem lies in motivating the agent to act in the principal’s interest rather than simply in the agent’s own interest.

